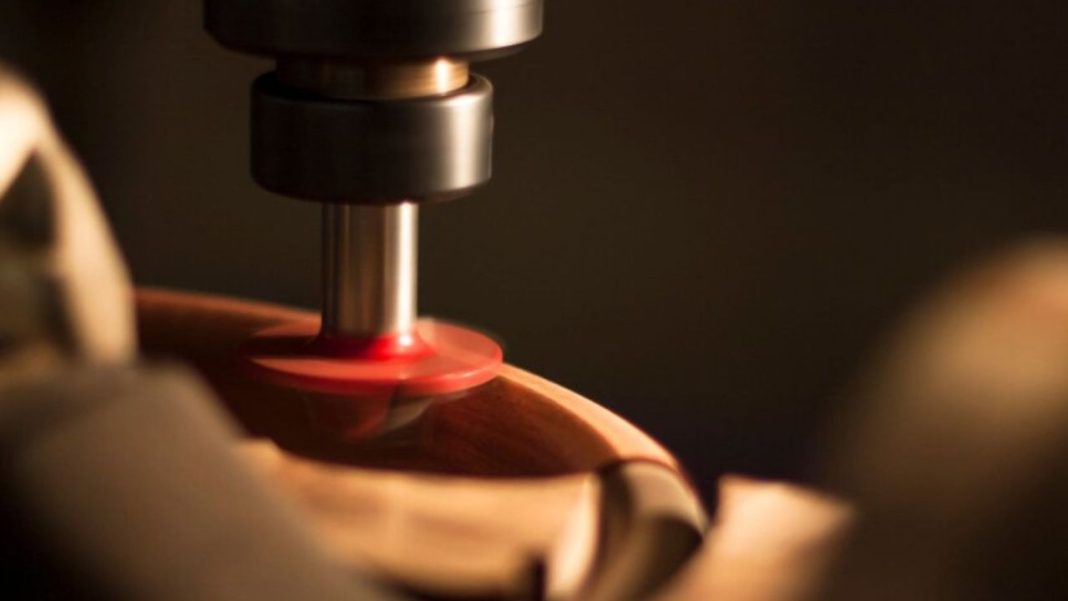
Manufacturers and CNC machining services are informed about the level of precision to be used while making an item by specified machining tolerances. More precision is needed the smaller the tolerance a tighter tolerance in the production industry. You need less precision the larger the tolerance, often known as the looser one. Tolerance standards are essential guidelines in CNC machining that specify the permissible range of variation in the shapes, sizes, and Different Types Machining Tolerances. These specifications are crucial in guaranteeing the operation, accuracy, and quality of the produced parts.
To put it briefly, tolerances are measurements that indicate the degree of accuracy required for an item you wish to produce. Tolerances for machining are measured by machinists using numerical values, usually indicated by a ± symbol. For instance, a part with a length of 2.550 inches might have a tolerance of ±0.001″. This would suggest that the length of the manufactured part would vary, ranging from 2.549″ to 2.551″. To pass quality inspection, the completed item should fall between 1.495″ and 1.505″ if a 1.5-inch tall part requires a tolerance of ±0.005″.
Standard Tolerances Are Frequently Applied In CNC Machining
In CNC machining, a number of common tolerance standards are used to guide the design, production, and inspection processes in order to satisfy specific requirements.
ISO Standards
Dimensions, geometrical features, and surface qualities are standardized worldwide by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). There are standards for general tolerances, limits, fits, and geometrical tolerances, such as ISO 2768, ISO 286; and ISO 8015.
GD&T – ASME Y14.5
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) is defined by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard Y14.5. Geometric tolerances are often specified with it, guaranteeing that pieces meet exact dimensions, forms, and orientations.
DIN Standards
To ensure uniform quality in production, the German Institute for Standardization (DIN) provides a range of tolerance standards, including DIN 7168, which focuses on general tolerances for linear and angular dimensions.
JIS Standards
To ensure consistency in production procedures, the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) offer requirements for a number of CNC machining-related topics, such as fits, tolerances, and limits.
These standards serve as a vital point of reference, guaranteeing that machined components meet predetermined shapes, dimensions, and surface finishes. This promotes consistency and accuracy in CNC production processes.
ANSI Standards
To guarantee that parts fulfill particular specifications, the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provides standards for a variety of businesses. These standards cover dimensional tolerances, fits, and surface roughness.
ASTM Standards
Materials and test procedures are governed by standards set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). These standards are essential to preserving material integrity, which affects tolerance adherence and machining.
NIST Handbook 44
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides weight and measure rules in Handbook 44. Although it isn’t exclusive to CNC machining, it guarantees consistency in the measurement systems employed in production.
BSI Standards
The British Standards Institution (BSI) publishes standards that guarantee products meet predetermined tolerances across a range of engineering and manufacturing specialties. Best practices for electrical safety, fire prevention, accuracy, repeatability testing, and safety are outlined in BSI standards for CNC machining. Machine shops may lower the risk of mistakes and accidents, increase quality, improve their reputation, and become more competitive by adhering to BSI standards.
MIL-STD (Military Standards)
Used in the aerospace and defense sectors, MIL-STD standards define the quality requirements and tolerances for components essential to military applications.
Industry-Specific Standards
Specific standards or requirements may vary throughout industries. For example, medical device makers might follow FDA regulations, whereas automobile manufacturers might adopt AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group) standards.
These common tolerance criteria guarantee that machined parts fit correctly into assemblies, fulfill quality standards, and follow specified specifications. Specific design considerations, part functioning, and industry requirements all play a role in the choice of standard.
Conclusion
Following these guidelines aids in production optimization, quality control, and guaranteeing that machined parts satisfy the necessary tolerances. In addition, these standards guarantee consistency and dependability in the CNC machining process by giving designers, manufacturers, and quality control staff a consistent language to communicate.